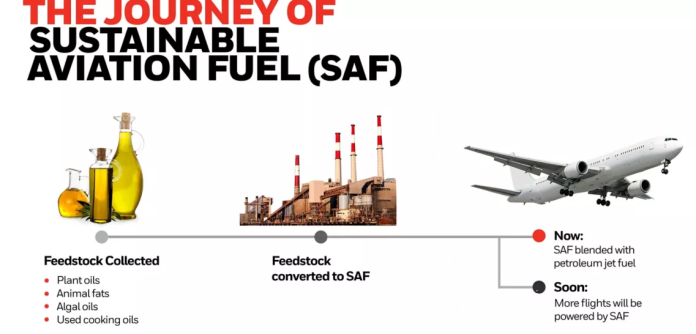
As the world grapples with climate change and environmental degradation, the aviation industry is under increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) has emerged as a critical solution to achieving climate-neutral air travel.
This blog post explores the intricacies of SAF, its benefits, production methods, challenges, and its role in the future of aviation.
What is Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)?
Sustainable Aviation Fuel is a type of alternative fuel specifically designed for aircraft, produced from non-petroleum feedstocks. SAF can be blended with conventional jet fuel and used in existing aircraft engines without modifications.
Its primary advantage lies in its potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels.
Read Also: WW Online: Your Path to Wellness | wight watchers com
- Compatibility: SAF can be blended with conventional jet fuel at varying percentages (up to 50% or more) depending on the production method and feedstock used.
- Emission Reductions: Depending on the feedstock and production pathway, SAF can reduce lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions by up to 94% compared to fossil fuels.
- Diverse Feedstocks: SAF can be produced from a variety of feedstocks, including waste oils, agricultural residues, and even algae.
The Importance of SAF in Aviation
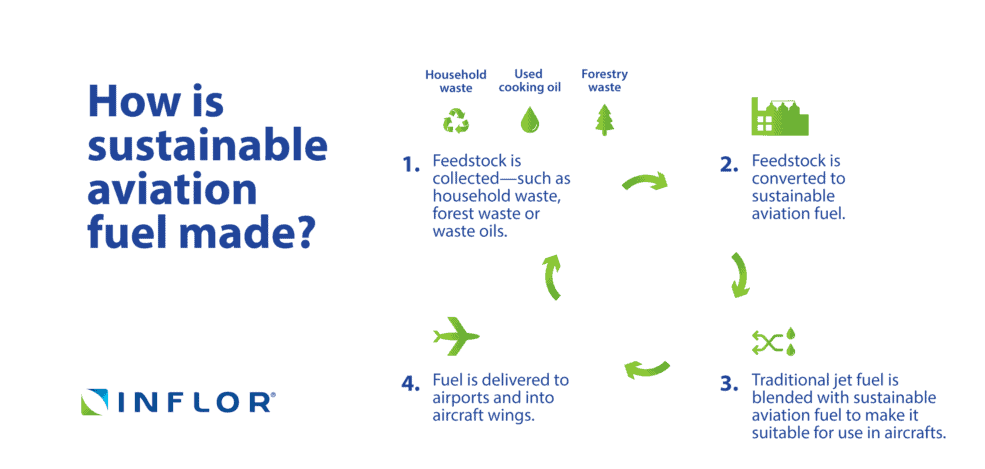
Aviation contributes approximately 2% of global carbon dioxide emissions, making it a significant player in the climate crisis. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has set ambitious targets for the aviation sector, aiming for net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
SAF is expected to play a pivotal role in achieving these goals, contributing between 53% and 71% of the necessary emissions reductions, according to the industry’s Waypoint 2050 analysis.
Production Pathways for SAF
SAF can be produced through several technological pathways, each with its unique processes and feedstocks. Here are some of the most prominent methods:
- Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids (HEFA): This method converts vegetable oils and animal fats into jet fuel through hydrogenation. It is currently the most widely used SAF production method.
- Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: This process converts biomass or waste feedstocks into synthetic fuels through gasification followed by chemical synthesis.
- Alcohol-to-Jet (ATJ): This method involves fermenting sugars from biomass into alcohols, which are then converted into jet fuel.
- Power-to-Liquid (PtL): Using renewable electricity, this process converts carbon dioxide and water into liquid hydrocarbons, offering a sustainable way to produce fuels.
Benefits of Sustainable Aviation Fuel
The adoption of SAF offers numerous advantages for the aviation sector:
- Environmental Impact: By significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions, SAF helps mitigate the aviation industry’s impact on climate change.
- Energy Security: Utilizing diverse feedstocks for fuel production reduces dependence on fossil fuels and enhances energy security.
- Economic Opportunities: The SAF market presents new business opportunities in agriculture, waste management, and renewable energy sectors.
- Regulatory Compliance: As governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations, SAF provides a pathway for airlines to comply with these mandates.
Challenges Facing SAF Adoption
Despite its potential, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of SAF:
- Cost: Currently, SAF is significantly more expensive than traditional jet fuel, often costing four times more. This economic barrier limits its market penetration.
- Production Capacity: The current production of SAF is low, constituting less than 1% of global aviation fuel consumption. Scaling up production to meet demand is essential.
- Infrastructure and Logistics: Existing fuel supply chains are primarily designed for fossil fuels, requiring significant investment to adapt to SAF.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape for SAF production and use can be challenging for new entrants in the market.
The Future of Sustainable Aviation Fuel
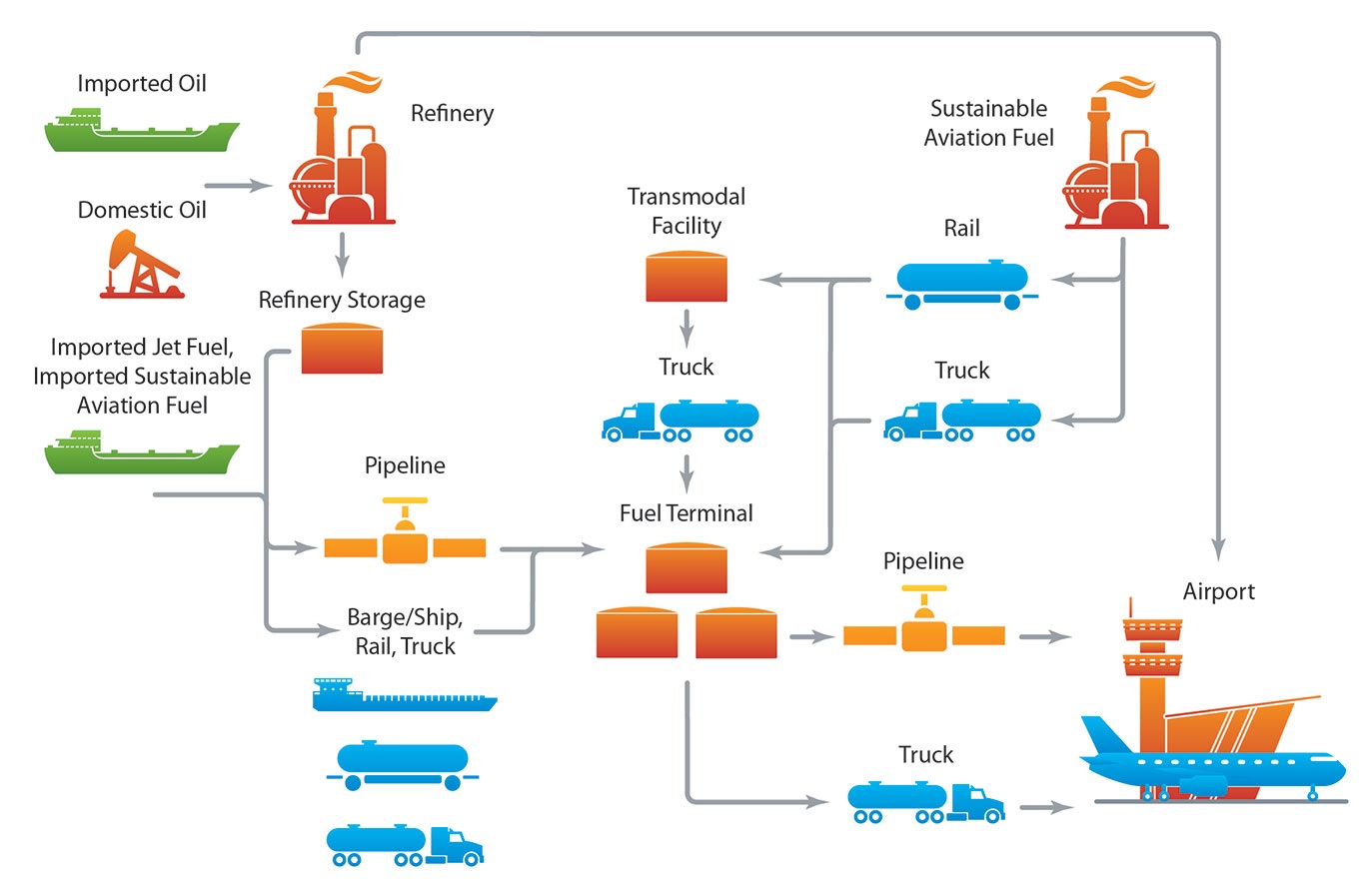
The future of SAF looks promising, driven by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory support, and growing environmental awareness among consumers. Key initiatives include:
- Government Incentives: Policies such as the Sustainable Skies Act in the U.S. aim to provide tax credits and financial support for SAF production, making it more economically viable.
- Industry Collaboration: Airlines, fuel producers, and governments are increasingly collaborating to develop SAF supply chains and production facilities.
- Research and Development: Ongoing R&D efforts focus on improving production efficiency, reducing costs, and expanding the range of feedstocks used for SAF.
Conclusion
Sustainable aviation fuel represents a significant step towards decarbonizing the aviation industry. While challenges remain, the collective efforts of governments, industry stakeholders, and researchers are paving the way for a more sustainable future in air travel.
By investing in SAF, the aviation sector can not only meet regulatory requirements but also fulfill its responsibility to combat climate change and protect the environment for future generations.
This comprehensive overview of sustainable aviation fuel aims to provide valuable insights into its significance, production methods, benefits, and challenges. By understanding the complexities of SAF, stakeholders can make informed decisions that contribute to a more sustainable aviation industry.